Home
June 8, 2022 2025-02-26 11:24Home
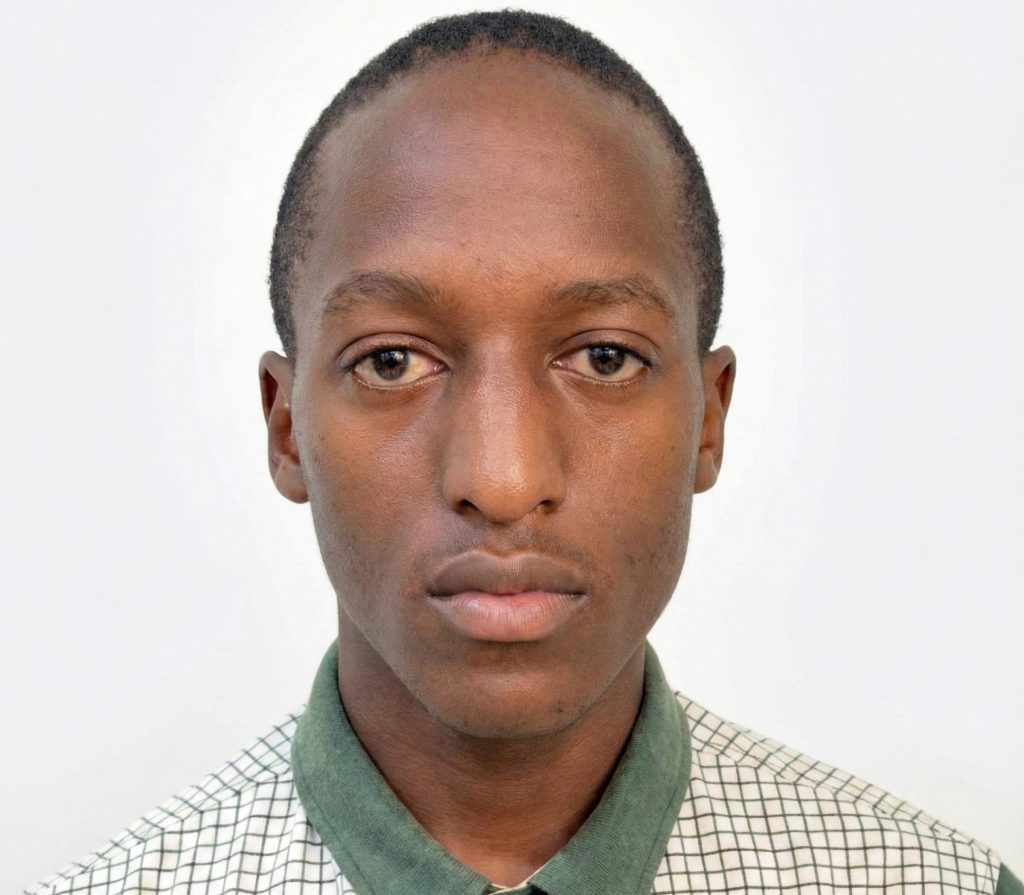
Mwangi Dennis Githinji’s Journey at Esri Eastern Africa
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 March 4, 2026
March 4, 2026
When Mwangi Dennis Githinji applied for the Esri Eastern Africa internship, he knew he was chasing more than just a…
Read More
Closing the Chapter on ArcMap
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 March 4, 2026
March 4, 2026
For more than 20 years, ArcMap has been a trusted tool for generations of GIS professionals worldwide. It helped map…
Read More
Meet the 2025 ArcGIS StoryMaps Competition Finalist
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 February 21, 2026
February 21, 2026
Esri Eastern Africa is excited to celebrate Grevy’s Zebra Trust’s Healthy Rangelands Program, named a finalist in the 2025 global…
Read More
Understanding ArcGIS Pro License Levels
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 February 6, 2026
February 6, 2026
Introduced in 2018, the user type model groups apps and capabilities to match the needs of different GIS roles.
Read More
A Guide to Smarter Sharing in ArcGIS
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 February 4, 2026
February 4, 2026
Imagine this: you’ve created a great collection of maps, web apps, and layers, all polished and ready. The final hurdle?
Read More
Got five minutes? Get to know Esri Updated Demographics
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 February 3, 2026
February 3, 2026
https://www.esri.com/arcgis-blog/products/esri-demographics/business/five-minutes-esri-updated-demographics
Read More
Press Release – Esri Eastern Africa Leadership Update
Everton Namasake has been promoted to the position of Acting Chief Commercial Officer effective 1st Jan 2026. Everton is a seasoned
Read More
What’s new across ArcGIS
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 January 20, 2026
January 20, 2026
ArcGIS continues to advance rapidly, rolling out new capabilities that help users work more efficiently, collaborate seamlessly, and unlock richer…
Read More
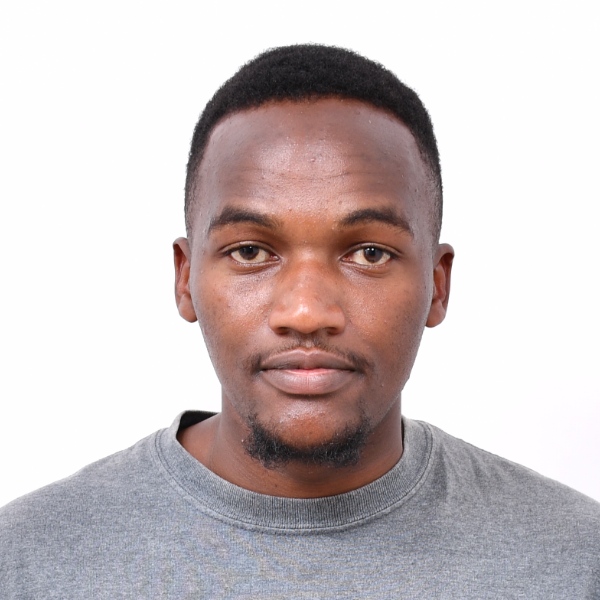
From Classroom Knowledge to Real-World Solutions
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 January 16, 2026
January 16, 2026
When Jackson Mbugua first applied to the Esri Eastern Africa internship program, he was driven by a clear goal: to…
Read More
Top 10 Things You May Not Know About ArcGIS Online
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 January 12, 2026
January 12, 2026
Top 10 Things You May Not Know About ArcGIS Online
Read More
Prepare for the Next Generation of ArcGIS Survey123
 Rachael Mutuli
Rachael Mutuli
 January 8, 2026
January 8, 2026
For years, ArcGIS Survey123 has been a trusted tool for organizations that depend on smart forms and reliable field data…
Read More
From Curiosity to Impact
At Esri Eastern Africa, our internship program is designed to expose students and young professionals to real-world geospatial problem-solving.
Read More