A Spatial Perspective for Resilient, Contemporary and Sustainable Infrastructure
August 30, 2022 2022-08-30 15:07A Spatial Perspective for Resilient, Contemporary and Sustainable Infrastructure
A Spatial Perspective for Resilient, Contemporary and Sustainable Infrastructure
One unappreciated advantage of digital transformation is its ability to connect data, merging knowledge that might otherwise languish in isolation. Combining datasets frequently results in knowledge that directly affects the integrity and safety of important infrastructure projects.
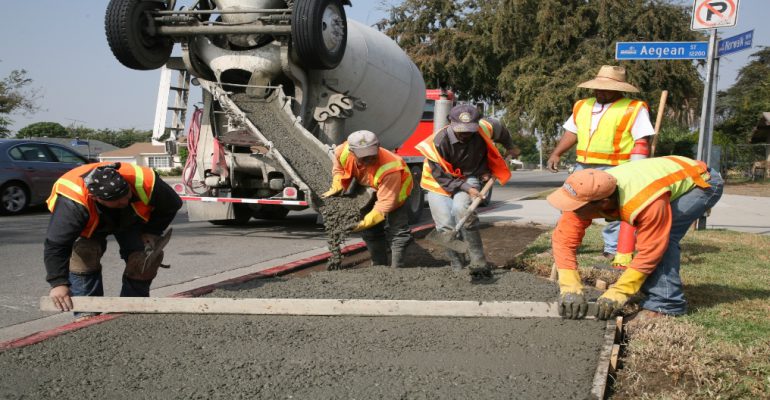
Using GIS technology, volumes of data, such as energy and transit networks, historical and projected usage, photography, sensor inputs, weather patterns, demographics, animal migration patterns, and native plant populations, can be layered on a smart map or dashboard and updated in real time.
When information is visualized on a map, people understand it better. A modern GIS enables enterprises to identify the precise location and specifics of every aspect of infrastructure, whether it’s above or below the ground or inside or outside of facilities. By using GIS technology to design, plan, visualize, and collaborate in real time through maps, dashboards, and applications, public and private infrastructure expenditures can be improved and optimized, preventing waste and inefficiency.
With spatial perspective already being used by decision-makers, and advanced geospatial technology, such as digital twins, sensors, and analytics, being incorporated into infrastructure systems, the future of infrastructure will be intelligent, data-centric, and dynamic.
GIS is also the best technology for setting goals and evaluating outcomes for sustainability, resilience, equity, safety, and efficiency since it offers a comprehensive and realistic view, down to hyperlocal details.
Importance of spatial perspective in ensuring a resilient and sustainable infrastructure
Here’s why tackling the life cycle of infrastructure initiatives requires a spatial approach:
- By using GIS-based modeling during the planning stage and geospatial analysis of imagery data throughout the building phase, new infrastructure can be delivered on time and within budget. You can count on the correct positioning of your assets to avoid needless drilling or digging to access subsurface infrastructure. Using a shared map to visualize cost and time calculations enables stakeholders to monitor and foresee the effects of changes and make necessary adjustments.
- Using GIS and building information modeling (BIM) as a single integrated system, helps you plan, construct, and manage infrastructure assets and projects during their full life cycle. GIS also improves data accuracy, by giving employees the ability to update information in real time through connected apps, doing away with paper-based processes or numerous systems. Using a location-enabled digital twin can help you predict maintenance and expansion of the infrastructure. GIS dashboards with important data and integrated analytics, visualized on a smart map, and findings that can be readily shared, can help AEC experts to find patterns and trends.
- Reduces carbon emissions by facilitating effective routes for vehicles, personnel, and goods in your logistics operations. Real-time awareness of a worker’s location can also reduce labor expenses for inspections and maintenance as well. Using GIS helps you gather, manage, and exchange information on a project or asset, then safely store it in the cloud to capture institutional knowledge about that asset or project.
- By employing predictive location analytics to fortify susceptible networks and plan expansion, you can deal with difficulties brought on by climate change, such as extreme weather, rising sea levels, and population migrations.
- Using a location-based system to gather data and comply with regulations, can help you manage dangers to people, property, and the environment. Infrastructure projects benefit from accurate maps and location analytics of performance and operations because they speed up repairs during service outages, save money because problems are addressed early on, enhance customer service, and keep employees safe.
- Using location intelligence can help you decide where to extend broadband or transit, how to safeguard neighborhoods from fire or flood, and when to update aged water systems. This will help you build important infrastructure equitably. Smart maps can be used by managers to find service coverage gaps, and spatial analysis can be used to rank upgrade priorities.
- Using GIS tools for automated inspection and maintenance can help you prioritize repair work and anticipate problems before they arise. You can use drones that can take pictures to assess hard-to-reach infrastructure while simultaneously teaching artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to spot problems that need to be fixed. GIS automates operations thus saving time during construction and continuing tasks, such as the ingestion and analysis of sensor and imagery data to a common map.
Are you looking for GIS solutions for your next project?
At Esri Eastern Africa we provide customers with working GIS solutions. Click here to purchase ArcGIS products online.